U.S. Healthcare Stakeholders Share Key Insights on the Future of NGS Adoption
As next-generation sequencing (NGS) becomes increasingly central to precision medicine, understanding stakeholder perspectives is critical. To evaluate current sentiment and near-term drivers of growth, we conducted a primary, online survey of 100 U.S.-based healthcare stakeholders, excluding patients.
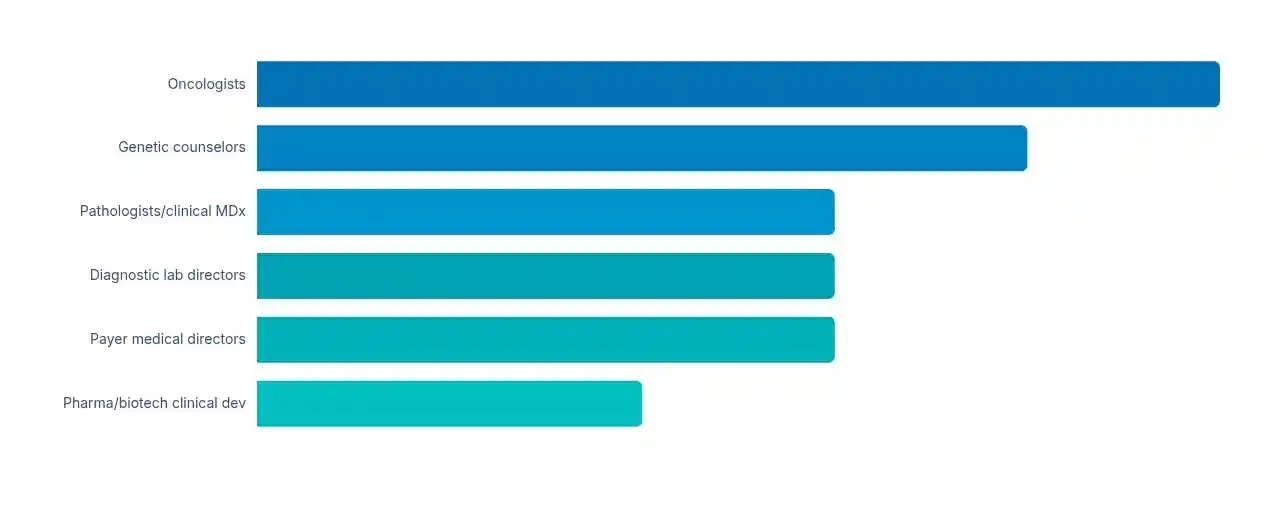
Stakeholders included oncologists, genetic counselors, pathologists, diagnostic lab leaders, payer medical directors, and pharma/biotech clinical development professionals.
Executive Summary
The study shows strong awareness and perceived clinical utility of NGS, particularly in oncology and rare disease diagnostics. However, key barriers—including reimbursement uncertainty, cost, and lack of standardized reporting—continue to limit scale. Respondents identified policy clarity, workflow integration, and improved real-world evidence as the most important levers for accelerating adoption in the next 12–36 months.
Respondent Profile
Study Objectives
- Measure awareness and perceived clinical utility of NGS.
- Identify current barriers limiting adoption.
- Assess near-term growth drivers and intent to expand use.
- Provide strategic recommendations for diagnostics companies, labs, and payers.
Methodology
- Design: Cross-sectional, online, self-administered survey
- Sample: 100 U.S. healthcare stakeholders
- Survey length: ~12–15 minutes
- Analysis: Descriptive statistics (percentages, cross-tabs)
- Ethics: Informed consent; anonymized responses
Key Findings
-
Strong Awareness and High Clinical Utility
- 90% are familiar with NGS
-
Clinical utility rated “moderate or high”:
o Oncology tumor profiling: 85%
o Rare disease diagnostics: 72%
o Hereditary cancer risk: 60%
o Cardiometabolic screening: 35%
-
Adoption Intent Is Strong
- 68% plan to increase NGS use within 12–24 months
- 60% of lab directors expect to invest in automation, LIMS, and bioinformatics systems
-
Barriers to Scale
Top cited barriers- Reimbursement complexity and inconsistent payer policies (60%)
- High cost (55%)
- Insufficient real-world evidence (50%)
- Lack of standardized reporting guidelines (40%)
- Turnaround time concerns (35%)
-
Growth Drivers for the Next 12–36 Months
Most important accelerators:- Clear and consistent payer coverage & reimbursement codes (70%)
- EHR integration with clinical decision support (65%)
- Lower test prices through economies of scale (60%)
- More real-world evidence and guideline endorsements (58%)
- Faster turnaround times via workflow improvements (45%)
-
Commercial Model Preferences
- 48% prefer send-out testing for complex panels
- 42% would develop in-house capability for rapid oncology decisions
-
Top vendor selection criteria:
o Strong clinical validation (82%)
o Reimbursement support and payer engagement (64%)
o Fast turnaround time (58%)
o Integration with LIMS/EHR systems (55%)
-
Stakeholder-Identified Unmet Needs
Common qualitative themes included:- Standardized payer engagement and prior authorization guidance
- More cost-effectiveness and outcome-focused evidence
- Simplified reporting formats with actionable summaries
- Scalable bioinformatics tools to reduce interpretation variability
Conclusion
NGS is viewed as clinically indispensable by U.S. healthcare stakeholders, particularly in oncology and rare disease. However, reimbursement clarity, workflow integration, and stronger real-world evidence remain essential to unlocking the next wave of adoption. Addressing these gaps will be critical for diagnostics companies, laboratories, and payers as the market continues to mature.
Our Global Clients
Our data-driven insights have influenced the strategy of 200+ reputed companies across the globe.