AI in Healthcare: US vs Europe Survey
1. Study Objective
Primary objective:
To assess how AI solutions in clinical and non-clinical hospital practices are changing care quality, efficiency, and workforce experience in hospitals in the US and Europe, based on responses from 100 frontline professionals.
Secondary objectives:
- Compare AI adoption patterns between US and European hospitals.
- Identify perceived benefits (diagnostic accuracy, time savings, cost efficiency, patient experience).
- Identify key barriers (data quality, integration, regulation, trust, skills).
- Explore differences between clinical staff (physicians, nurses, allied health) and non-clinical staff (administration, IT, operations).
2. Methods – How your 100-respondent survey could look
- Design: Cross-sectional online survey.
-
Sample:
- N = 100 hospital professionals
- 60 from the US, 40 from Europe (e.g., EU + UK, Switzerland)
- 65% clinical roles, 35% non-clinical/administrative/IT
- Key sections in the questionnaire:
- Demographics & role (country, hospital type, role, years of experience).
-
AI exposure & adoption:
- “Does your hospital currently use AI in clinical care?” (Yes/No)
- “In which areas is AI used?” (diagnostic imaging, triage, CDSS, documentation, scheduling, billing, supply chain, bed management, chatbots, etc.)
-
Perceived impact (5-point Likert scale, then collapsed into positive/neutral/negative):
- Diagnostic accuracy
- Time to diagnosis / throughput
- Administrative workload
- Patient experience & access
- Staff burnout
- Barriers & risks (data quality, bias, explainability, regulation, cost, IT integration, training).
- Future outlook (likelihood of increasing AI use in next 3–5 years).
3. Example Outcomes with Data (Illustrative)
3.1 Respondent profile & adoption
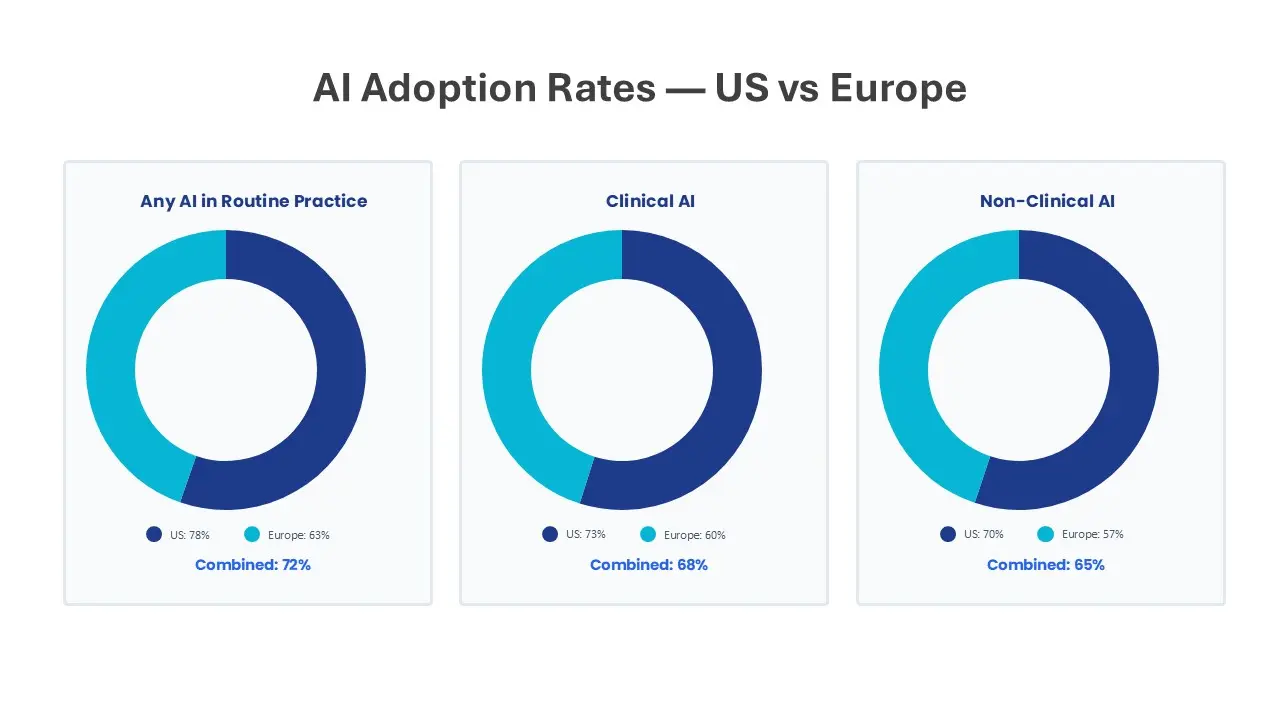
Table 1. Respondent profile and AI adoption (N = 100)
| Characteristic | Overall (N=100) | US (n=60) | Europe (n=40) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical roles (physicians, nurses, etc.) | 65% | 63% | 68% |
| Non-clinical (admin, IT, operations, finance) | 35% | 37% | 32% |
| Hospital uses any AI in routine practice | 72% | 78% | 63% |
| Uses clinical AI (diagnostics, CDSS, etc.) | 68% | 73% | 60% |
| Uses non-clinical AI (admin/ops/finance) | 65% | 70% | 57% |
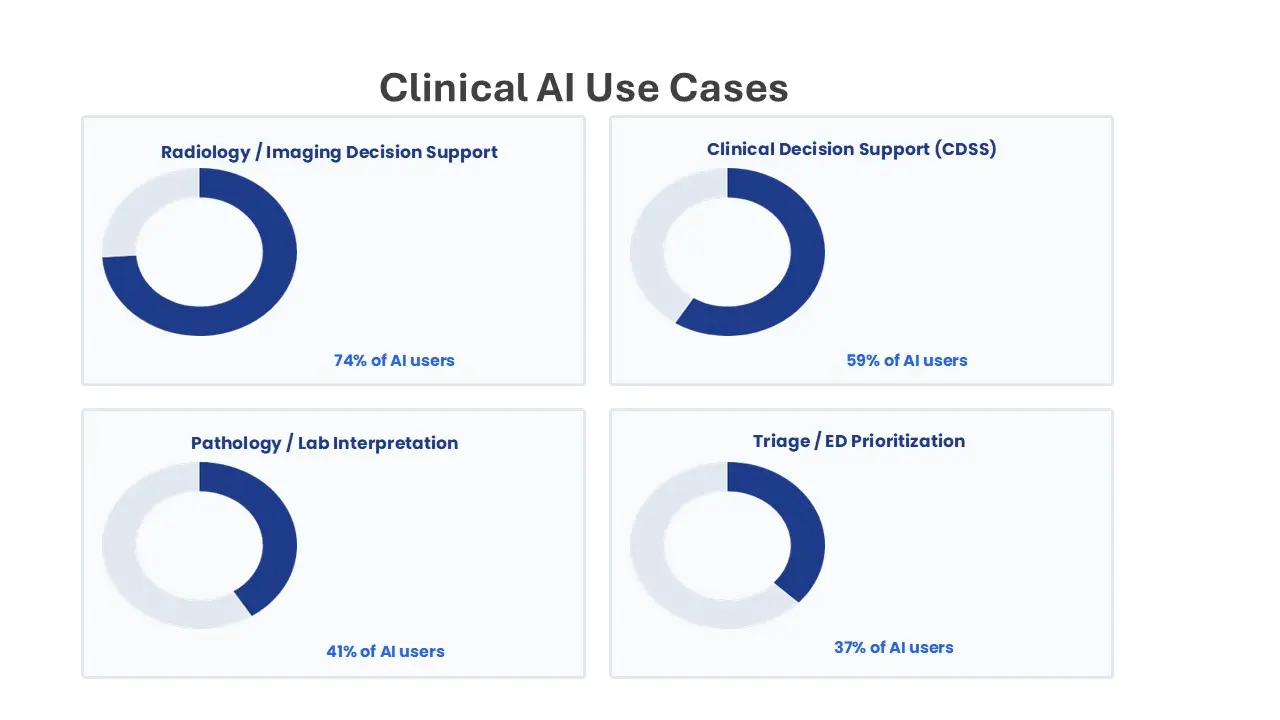
Top clinical AI use-cases (among hospitals using clinical AI)
- Radiology / imaging decision support (e.g., triage, detection, quantitative reporting): 74%
- Clinical decision support (risk scores, sepsis alerts, treatment suggestions): 59%
- Pathology / lab interpretation: 41%
- Triage / ED prioritization: 37%
Top non-clinical AI use-cases (among hospitals using non-clinical AI)
- Appointment scheduling & no-show prediction: 61%
- Billing & coding automation / denial management: 54%
- Bed management & patient flow prediction: 46%
- Supply chain & inventory optimization: 33%
3.2 Perceived impact of AI (aggregated outcomes)
You can report your primary outcomes as % of respondents reporting “positive” or “strongly positive” impact.
Table 2. Perceived impact of AI among users (n ≈ 72 who report active AI use)
| Outcome domain | US (%) | Europe (%) | Combined (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic accuracy (clinical AI) | 71 | 66 | 69 |
| Time to diagnosis / throughput | 76 | 70 | 74 |
| Reduction in admin workload | 63 | 58 | 61 |
| Patient access & experience | 55 | 52 | 54 |
| Staff burnout / cognitive load | 49 | 45 | 47 |
| Overall quality of care | 68 | 64 | 66 |
These directions are in line with empirical findings showing:
- Imaging & diagnostics AI → higher accuracy and shorter reading times without replacing clinicians.
- Clinical decision support AI → improved diagnostic confidence and reduced diagnostic time in internal medicine.
- Admin AI → fewer billing errors, faster scheduling, and better throughput.
- Operations / resource AI → better bed utilization and capacity planning in European systems.
3.3 Barriers and risks (secondary outcomes)
You can also show data like:
Table 3. Top reported barriers to AI adoption (multiple responses allowed, % of all respondents)
| Barrier / concern | US (%) | Europe (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Data integration / EHR interoperability | 58 | 62 |
| Lack of transparency / explainability of models | 45 | 53 |
| Regulatory / legal uncertainty | 39 | 67 |
| Concerns about algorithmic bias & equity | 42 | 50 |
| Upfront cost and unclear ROI | 47 | 44 |
| Lack of training / digital skills | 51 | 48 |
These are consistent with EU and US analyses, which highlight data quality, bias, explainability, regulation (especially in EU), and workforce readiness as key barriers.

4. How this fits US vs European perspective
United States
- Rapid experimentation with generative AI and EHR-integrated tools (e.g., ambient documentation, summarization, note drafting) and broader piloting across large health systems.
- Stronger focus on operational ROI (throughput, revenue cycle, staffing) and tackling physician burnout.
Europe
- Slightly slower but steady uptake, with strong emphasis on regulation, ethics, and patient safety under the EU’s AI regulatory framework.
- More central focus on public health systems, interoperability across regions, and equity, and high interest in AI for resource allocation, virtual care, and population health.
Companies – Clinical / diagnostic & imaging AI
- Aidoc – enterprise clinical AI platform for radiology and multi-specialty triage and decision support; widely deployed in US and Europe.
- RapidAI – stroke, PE and vascular AI with a strong care coordination and imaging platform.
- Qure.ai – imaging AI (chest X-ray, CT brain, TB, lung cancer), active in Europe and globally.
- GE HealthCare – imaging and AI-enabled enterprise platforms; recent acquisition of Intelerad to strengthen cloud imaging + AI strategy.
- Siemens Healthineers – AI-Rad Companion, AI-enabled scanners, and enterprise imaging AI ecosystem (global, including EU & US).
- Philips – AI-enhanced enterprise imaging, patient monitoring and acute-care decision support.
- Canon Medical – decision support & AI platforms for multimodal clinical data.
- Agfa HealthCare (RUBEE AI) – AI embedded in enterprise imaging and radiology workflows.
- deepc (Europe) – AI “operating system” for imaging, hosting multiple algorithms with enterprise governance and orchestration.
Our Global Clients
Our data-driven insights have influenced the strategy of 200+ reputed companies across the globe.